Vacuum Suction Cups: Material Properties, Design Types, and System Components for Engineers Vacuum suction cups are essential components in modern automation, robotics, and material-handling systems. From pick-and-place machines in electronics to automotive assembly lines and pharmaceutical packaging, these simple yet powerful devices enable efficient gripping, lifting, and moving of workpieces. For engineers, selecting the right suction cup requires a deep understanding of material properties, design types, and system components. This guide provides a detailed breakdown to help professionals make informed choices for reliable and efficient applications. 1. Suction Cup Materials and Their Applications Different environments and workpiece surfaces demand specific material properties. Engineers should carefully match the suction cup material with the application conditions: Nitrile Rubber (NBR) Ideal for: General-purpose use in industrial handling. Properties: Good resistance to oils and grease, moderate temperature range. Temperature Range: -10°C to +70°C. Applications: Packaging, logistics, and general automation tasks. Silicone Rubber (VMQ) Ideal for: High-temperature and food-grade applications. Properties: Excellent flexibility, high thermal resistance, FDA-compliant for food contact. Temperature Range: -30°C to +200°C. Applications: Food processing, medical devices, handling uneven or textured surfaces. Polyurethane (PU) Ideal for: High wear-resistance environments. Properties: Durable, abrasion-resistant, and maintains grip on rough or porous surfaces. Applications: Woodworking, metal stamping, carton and corrugated board handling. Viton (FKM) Ideal for: Harsh industrial and chemical environments. Properties: Superior resistance to oils, fuels, aggressive chemicals, and elevated temperatures. Temperature Range: -20°C to +200°C. Applications: Automotive, aerospace, chemical processing, and high-demand industrial automation. 2. Suction Cup Design Types The geometry of a suction cup directly affects performance. Choosing the correct shape ensures a secure grip and reduces the risk of slippage or damage to parts. Flat Suction Cups Best for: Smooth, flat, or slightly curved surfaces. Advantages: High stability, fast release, and strong holding power. Variants: Standard lips for rigid surfaces, thin lips for flexible or delicate parts. Bellows Suction Cups Best for: Uneven, curved, or fragile workpieces. Advantages: Compensate for height variations, absorb shocks, and provide gentle handling. Applications: Glass, electronics, or irregularly shaped plastic components. Oval Suction Cups Best for: Narrow, elongated, or rectangular workpieces. Advantages: Maximize contact on limited surface areas, ideal for long objects. Applications: Automotive bumpers, sheet metal strips, packaging films. 3. Complete Vacuum System Components A suction cup does not operate alone. For a reliable vacuum handling solution, engineers must consider the entire system: Vacuum Generators: Includes vacuum pumps and ejectors that create the required suction force. Filters: Prevent dust, debris, or contaminants from entering the system and damaging pumps or ejectors. Tubing & Connectors: Ensure proper air flow and minimal leakage. High-quality fittings are essential for stable performance. Control Valves & Sensors: Allow precise regulation, monitoring, and automation of vacuum operations. By integrating these components effectively, engineers can build efficient vacuum handling systems tailored to their production needs. 4. Key Takeaways for Engineers Material selection ensures compatibility with environment and surface type. Design type influences stability, speed, and adaptability to workpiece geometry. System integration with filters, ejectors, and tubing ensures long-term reliability. Vacuum suction cups may seem like simple devices, but choosing the correct combination of material, design, and system components can significantly improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and extend equipment lifespan. Product Keywords to target: Vacuum suction cups, industrial suction cups, pneumatic suction cups, automation gripping solutions, suction cup materials, bellows suction cups, oval suction cups, flat suction cups, vacuum handling systems, vacuum generators.
Chat with us on WhatsApp
×
This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
https://www.ibizkart.in/visakhapatnam/latest-update/vacuum-suction-cups-material-properties-design-types-and-system-components-for-engineers-vacuum/1011
Vacuum Suction Cups: Material Properties, Design Types, and System Components for Engineers Vacuum...

2025-10-03T16:10:57
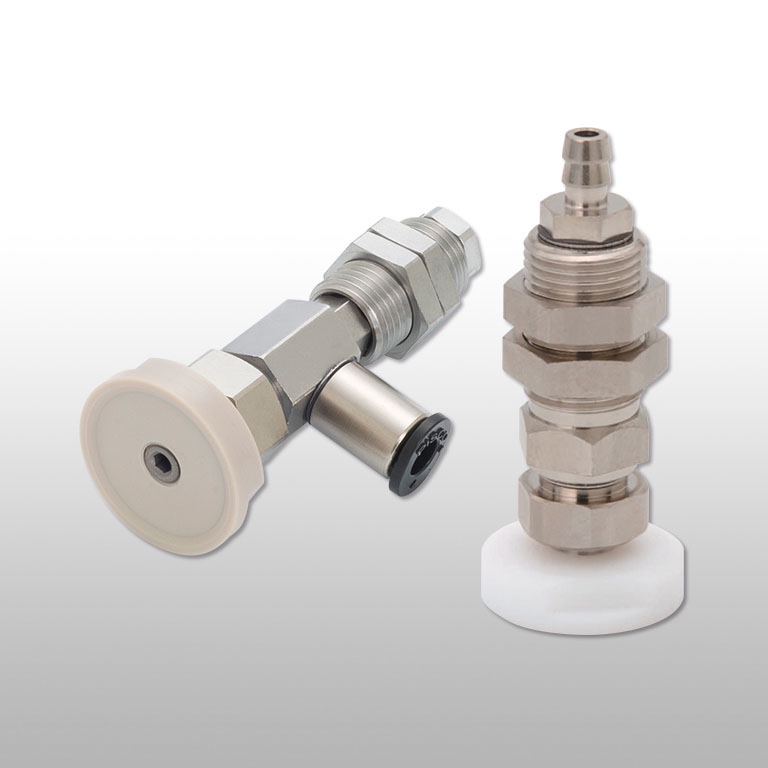
Vacuum Suction Cups: Material Properties, Design Types, and System Components for Engineers Vacuum suction cups are essential components in modern automation, robotics, and material-handling systems. From pick-and-place machines in electronics to automotive assembly lines and pharmaceutical packaging, these simple yet powerful devices enable efficient gripping, lifting, and moving of workpieces. For engineers, selecting the right suction cup requires a deep understanding of material properties, design types, and system components. This guide provides a detailed breakdown to help professionals make informed choices for reliable and efficient applications. 1. Suction Cup Materials and Their Applications Different environments and workpiece surfaces demand specific material properties. Engineers should carefully match the suction cup material with the application conditions: Nitrile Rubber (NBR) Ideal for: General-purpose use in industrial handling. Properties: Good resistance to oils and grease, moderate temperature range. Temperature Range: -10°C to +70°C. Applications: Packaging, logistics, and general automation tasks. Silicone Rubber (VMQ) Ideal for: High-temperature and food-grade applications. Properties: Excellent flexibility, high thermal resistance, FDA-compliant for food contact. Temperature Range: -30°C to +200°C. Applications: Food processing, medical devices, handling uneven or textured surfaces. Polyurethane (PU) Ideal for: High wear-resistance environments. Properties: Durable, abrasion-resistant, and maintains grip on rough or porous surfaces. Applications: Woodworking, metal stamping, carton and corrugated board handling. Viton (FKM) Ideal for: Harsh industrial and chemical environments. Properties: Superior resistance to oils, fuels, aggressive chemicals, and elevated temperatures. Temperature Range: -20°C to +200°C. Applications: Automotive, aerospace, chemical processing, and high-demand industrial automation. 2. Suction Cup Design Types The geometry of a suction cup directly affects performance. Choosing the correct shape ensures a secure grip and reduces the risk of slippage or damage to parts. Flat Suction Cups Best for: Smooth, flat, or slightly curved surfaces. Advantages: High stability, fast release, and strong holding power. Variants: Standard lips for rigid surfaces, thin lips for flexible or delicate parts. Bellows Suction Cups Best for: Uneven, curved, or fragile workpieces. Advantages: Compensate for height variations, absorb shocks, and provide gentle handling. Applications: Glass, electronics, or irregularly shaped plastic components. Oval Suction Cups Best for: Narrow, elongated, or rectangular workpieces. Advantages: Maximize contact on limited surface areas, ideal for long objects. Applications: Automotive bumpers, sheet metal strips, packaging films. 3. Complete Vacuum System Components A suction cup does not operate alone. For a reliable vacuum handling solution, engineers must consider the entire system: Vacuum Generators: Includes vacuum pumps and ejectors that create the required suction force. Filters: Prevent dust, debris, or contaminants from entering the system and damaging pumps or ejectors. Tubing & Connectors: Ensure proper air flow and minimal leakage. High-quality fittings are essential for stable performance. Control Valves & Sensors: Allow precise regulation, monitoring, and automation of vacuum operations. By integrating these components effectively, engineers can build efficient vacuum handling systems tailored to their production needs. 4. Key Takeaways for Engineers Material selection ensures compatibility with environment and surface type. Design type influences stability, speed, and adaptability to workpiece geometry. System integration with filters, ejectors, and tubing ensures long-term reliability. Vacuum suction cups may seem like simple devices, but choosing the correct combination of material, design, and system components can significantly improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and extend equipment lifespan. Product Keywords to target: Vacuum suction cups, industrial suction cups, pneumatic suction cups, automation gripping solutions, suction cup materials, bellows suction cups, oval suction cups, flat suction cups, vacuum handling systems, vacuum generators.
2025-10-03T16:10:57
Keywords
- High-temperature resistant silicone rubber suction cups
- Suction cups for automotive assembly lines
- System integration with vacuum generators
- Suction cup materials for food-grade use
- Vacuum handling systems components
- Flat suction cups for smooth surfaces
- Bellows suction cups for fragile parts
- Pneumatic suction cups applications
- Industrial suction cups material properties
- Vacuum suction cups for automation

Submit Your Enquiry